What is a computer?
Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as an input from the user and processes it under the control of a set of instructions (called program), produces a result (output), and saves it for future use. This tutorial explains the foundational concepts of computer hardware, software, operating systems, peripherals, etc. along with how to get the most value and impact from computer technology.
Functionalities of a Computer
There are three basic functionalities of a Computer System and they are
- 1. Input
- 2. Process
- 3. Output
But if we look at it in a very broad sense, any digital computer carries out the following five functions:
- Step 1 - Takes data as input.
- Step 2 - Stores the data/instructions in its memory and uses them as required.
- Step 3 - Processes the data and converts it into useful information.
- Step 4 - Generates the output.
- Step 5 - Controls all the above four steps.
Advantages of Computers
Following are certain advantages of computers.
High Speed
- Computer is a very fast device.
- It is capable of performing calculation of very large amount of data.
- The computer has units of speed in microsecond, nanosecond, and even the picosecond.
- It can perform millions of calculations in a few seconds as compared to man who will
- spend many months to perform the same task.
Accuracy
- In addition to being very fast, computers are very accurate.
- The calculations are 100% error free.
- Computers perform all jobs with 100% accuracy provided that the input is correct.
Storage Capability
- Memory is a very important characteristic of computers.
- A computer has much more storage capacity than human beings.
- It can store large amount of data.
- It can store any type of data such as images, videos, text, audio, etc.
Versatility
- A computer is a very versatile machine.
- A computer is very flexible in performing the jobs to be done.
- This machine can be used to solve the problems related to various fields.
- At one instance, it may be solving a complex scientific problem and the very next moment it may be playing a card game.
Reliability
- A computer is a reliable machine.
- Modern electronic components have long lives.
- Computers are designed to make maintenance easy.
Automation
- Computer is an automatic machine.
- Automation is the ability to perform a given task automatically. Once the computer receives a program i.e., the program is stored in the computer memory, then the program and instruction can control the program execution without human interaction.
Reduction in Paper Work and Cost
- The use of computers for data processing in an organization leads to reduction in paper work and results in speeding up the process.
- As data in electronic files can be retrieved as and when required, the problem of maintenance of large number of paper files gets reduced.
- Though the initial investment for installing a computer is high, it substantially reduces the cost of each of its transaction.
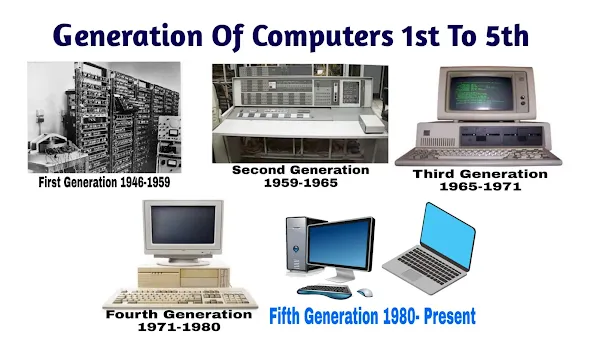
Generations of Computers
Generation in computer terminology is a change in technology a computer is/was being used. Initially, the generation term was used to distinguish between varying hardware technologies. Nowadays, generation includes both hardware and software, which together make up an entire computer system. There are five computer generations known till date. Each generation has been discussed in detail along with their time period and characteristics. In the following table, approximate dates against each generation has been mentioned, which are normally accepted. Following are the main five generations of computers
Generation & Description
First Generation
The period of first generation: 1946-1954. Vacuum tube based.
Second Generation
The period of second generation: 1955-1965. Transistor based.
Third Generation
The period of third generation: 1965-1971. Integrated Circuit based.
Fourth Generation
The period of fourth generation: 1971-1980. VLSI microprocessor based.
Fifth Generation
The period of fifth generation: 1980-onwards. ULSI microprocessor based.
First Generation Computers
The period of first generation was from 1946-195. The computers of first generation used vacuum tubes as the basic components for memory and circuitry for CPU (Central Processing Unit). These tubes, like electric bulbs, produced a lot of heat and the installations used to fuse frequently. Therefore, they were very expensive and only large organizations were able to afford it.
In this generation, mainly batch processing operating system was used. Punch cards, paper tape, and magnetic tape was used as input and output devices. The computers in this generation used machine code as the programming language.
The main features of the first generation are:
• Vacuum tube technology
• Unreliable
• Supported machine language only
• Very costly
• Generates lot of heat
• Slow input and output devices
• Huge size
• Need of AC
• Non-portable
• Consumes lot of electricity
Some computers of this generation were:
• ENIAC
• EDVAC
• UNIVAC
• IBM-701
• IBM-750
Second Generation Computers
The period of second generation was from 1955-1965. In this generation, transistors were used
that were cheaper, consumed less power, more compact in size, more reliable and faster than
the first-generation machines made of vacuum tubes. In this generation, magnetic cores were
used as the primary memory and magnetic tape and magnetic disks as secondary storage
devices.
In this generation, assembly language and high-level programming languages like FORTRAN,
COBOL were used. The computers used batch processing and multiprogramming operating
system.
The main features of second generation are:
• Use of transistors
• Reliable in comparison to first generation computers
• Smaller size as compared to first generation computers
• Generates less heat as compared to first generation computers
• Consumed less electricity as compared to first generation computers
• Faster than first generation computers
• Still very costly
• AC required
• Supported machine and assembly languages
Some computers of this generation were:
• IBM 1620
• IBM 7094
• CDC 1604
• CDC 3600
• UNIVAC 1108
Third Generation Computers
The period of third generation was from 1965-1971. The computers of third generation used
Integrated Circuits (ICs) in place of transistors. A single IC has many transistors, resistors, and capacitors along with the associated circuitry.
The IC was invented by Jack Kilby. This development made computers smaller in size, reliable, and efficient. In this generation remote processing, time-sharing, multi-programming operating system were used. High-level languages (FORTRAN-II TO IV, COBOL, PASCAL PL/1, BASIC, ALGOL-68 etc.) were used during this generation.
The main features of third generation are:
• IC used
• More reliable in comparison to previous two generations
• Smaller size
• Generated less heat
• Faster
• Lesser maintenance
• Costly
• AC required
• Consumed lesser electricity
• Supported high-level language
Some computers of this generation were:
• IBM-360 series
• Honeywell-6000 series
• PDP (Personal Data Processor)
• IBM-370/168
• TDC-316
Fourth Generation Computers
The period of fourth generation was from 1971-1980. Computers of fourth generation used Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits. VLSI circuits having about 5000 transistors and
other circuit elements with their associated circuits on a single chip made it possible to have microcomputers of fourth generation.
Fourth generation computers became more powerful, compact, reliable, and affordable. As a result, it gave rise to Personal Computer (PC) revolution. In this generation, time sharing, real
time networks, distributed operating system were used. All the high-level languages like C, C++, DBASE etc., were used in this generation.
The main features of fourth generation are:
• VLSI technology used
• Very cheap
• Portable and reliable
• Use of PCs
• Very small size
• Pipeline processing
• No AC required
• Concept of internet was introduced
• Great developments in the fields of networks
• Computers became easily available
Some computers of this generation were:
• DEC 10
• STAR 1000
• PDP 11
• CRAY-1(Super Computer)
• CRAY-X-MP(Super Computer)
Fifth Generation Computers
The period of fifth generation is 1980-till date. In the fifth generation, VLSI technology became ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology, resulting in the production of microprocessor chips having ten million electronic components.
This generation is based on parallel processing hardware and AI (Artificial Intelligence) software. AI is an emerging branch in computer science, which interprets the means and method of making computers think like human beings. All the high-level languages like C and C++, Java, .Net etc., are used in this generation.
The main features of fifth generation are:
• ULSI technology
• Development of true artificial intelligence
• Development of Natural language processing
• Advancement in Parallel Processing
• Advancement in Superconductor technology
• More user-friendly interfaces with multimedia features
• Availability of very powerful and compact computers at cheaper rates
Some computer types of this generation are:
• Desktop
• Laptop
• Notebook
• Ultrabook
• Chromebook



Comments
Post a Comment