Flow Charts
Flow charts are a
useful tool in many situations, as we make a process easy to understand at a
glance. Using just a few words and some simple symbols, they show clearly what
happens at each stage and how this affects other decisions and actions.
What
Is a Flow Chart?
In 1921, the Frank
and Lillian presented what was only a "graphic-based method" in a
presentation titled: “Process Charts:
First Steps in Finding the One Best Way to do Work”, to members of the
American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME).
Flowchart is a very simple yet powerful tool to improve
productivity in both our personal and work life. Here are some ways flowchart
can be helpful:
· Document
a process
· Present
solution to a problem
· Brainstorm
ideas in a meeting
· Design
an operation system
· Explain
a decision making process
· Store
information
· Draw
an organizational chart
· Create
a visual user journey
· Create
a sitemap
Flowchart
Symbols & Components
Flowchart Symbols
1. Flowline: Shows the step's direction. Each flow line
connects two blocks. This component is represented by lines with arrows
indicating the flow's direction. Users can also add text on top of flow line to
add more context to the step.
2.
Terminal
Symbol: Indicates the
beginning or end of a flowchart. This symbols is indicated by the oval shape.
Often, you'll see the
word "Start" or "End" in a terminal component. In a large
flowchart, having terminal symbols helps users quickly identify where the
flowchart begins so they can actually begin reading the process.
3. Process Symbol: Represent a step in a process. This is the most common component of a flowchart. Process symbol is represented by the rectangle shape.
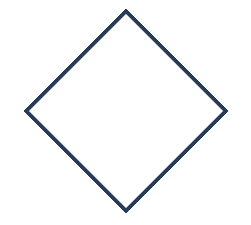
4. Decision Symbol: Shows a step that decides the next step
in a process. This is commonly a yes/no or true/false question. Decision is
represented by the diamond shape
Typically, from this decision symbol, there will be two flow lines
that branch out. Often, these flow lines will have the texts "Yes" and
"No", indicating the decision to be made.
5. Input / Output Symbol: Indicates the process of inputting or
outputting external data. Input / Output is represented by the parallelogram
shape.
6. Annotation / Comment: Indicates additional information regarding a
step in a process.
7. Predefined Process: Shows named process which is defined
elsewhere.
8. On-page Connector: Pairs of on-page connecter
are used to replace long lines on a flowchart page.
How to create a flowchart
Step 1: Map out major steps
In most
cases, you can start with terminal symbol, and start drawing more process symbols (rectangles) for the
next steps, and continue working your way through the end of the process.
Because flowcharts are read left to right and top to bottom, make sure to draw your terminal
symbol at the top left corner of your workspace.
Step 2: Input the details
Fill in the
remaining steps. We recommend working in the natural order of the process. An
optional step here is to style your chart with different shapes and color to
make it easier to follow.
Step 3: Test your result
Work through
all the steps in your chart to make sure they are clear and exhaustive, and
that there is no unintended open-ended node remained. When there is a decision
point, make sure the options cover all possible scenarios.
Step 4: Gather feedback on your flow chart
Share a draft
of the flowchart and get feedback from the intended users. If the flow chart is
meant just for yourself then you can skip this step. But if the chart is meant
for a team or a group of people, then it’s important to get their feedback to
make sure that your flowchart is accurate and helpful.
Step 5: Publish the flowchart
Flowcharts
should be made easily accessible to all parties involved. So make sure you
publish your work in the right place.
Types of Flowcharts
·
Process Flowchart
·
Process Map
·
Process Flow Diagram
·
Workflow Chart
·
Workflow Diagram
·
Data Flow Diagram
·
System Flowchart
Examples of Flow Chart
Add 2 no input from user.















Comments
Post a Comment